Phosphorus
Health benefits of Phosphorus:
Contributes to the normal function of all your cells, your energy creation, helps maintain the health of your bones and teeth and promotes the normal growth of children
The Worlds Science
See the bottom of this page for the ingredients highest in phosphorus.
What is Phosphorus?
Phosphorus is a non-metallic essential element that comes in two main forms:
- White phosphorus is a poisonous waxy solid and contact with skin can cause severe burns. It also glows in the dark and ignites in air!
- Red phosphorus is a much less reactive, non-toxic solid1.
Phosphorus combines with organic molecules to form ('dietary') phosphorus and is found in the cells of plants and animals.
Why does it matter to me?
- Phosphorus is a component of a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This molecule is used to transfer energy inside every cell of your body2.
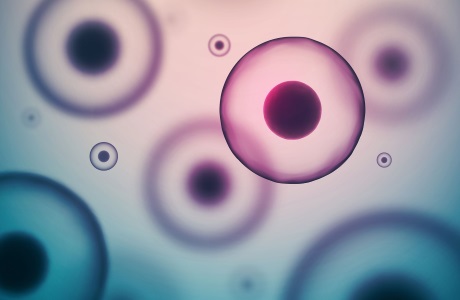
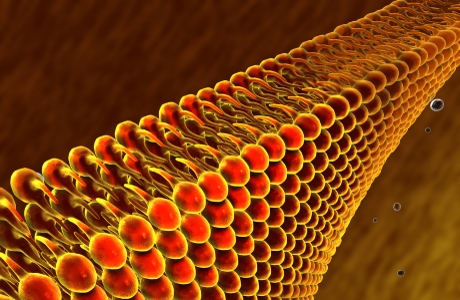
- All cells are surrounded by ‘membranes’ which control every atom, molecule, compound and drug that moves into or out of them3.
- Phosphorus is also a structural component of both DNA and RNA, the molecules of inheritance which are required for cell growth and reproductive success4.
How phosphorus reacts with...
Of the total body stores of phosphate, 85% are deposited in bones and teeth where it associates with calcium in the form of hydroxyapatite (a form of calcium phosphate). Therefore, phosphorus is essential for the development of healthy bones and teeth in children and their maintenance in adults5,6.
What are the best sources?
Phosphorus is found in all naturally occurring food because it is an essential mineral for all living organisms. Dairy foods, cereal products, meat and fish are particularly rich sources of phosphorus.
The phosphorus in plant seeds (beans, peas, cereals, and nuts) is present in a storage form of phosphate called phytate. However, only about 50% of the phosphorus from phytate is available to humans because we lack enzymes (phytases) that remove phosphorus from phytate.
Yeasts possess phytases, so whole grains incorporated into leavened breads have more bio available phosphorus than whole grains incorporated into breakfast cereals or flat breads7,8.
What happens if I don’t get enough?
Because phosphorus is so widely present in the diet, serious deficiency symptoms are extremely rare and only observed in people with certain medical conditions such as alcoholism.
However, if you don’t have enough phosphorus it can results in loss of appetite, mild muscle weakness and may also increase your susceptibility to infection9.
Review date: 2/9/2022
Next review date: 2/9/2023
291
445
https://www.checkyourfood.com/content/blob/Micronutrients/top-foods-for-Phosphorus.jpg
Top 6 ingredients for Phosphorus taking into account portion size and cooking retention factors
Filter ingredients by:

 About nutrients
About nutrients
 All nutrients
All nutrients
 vitamins
vitamins
 minerals
minerals
 phytochemicals
phytochemicals
 fatty acids
fatty acids
 macronutrients
macronutrients
 amino acids
amino acids