Potassium
Health benefits of Potassium:
Contributes to keeping your blood pressure normal, your nervous system functioning well and your muscles working properly
The Worlds Science
See the bottom of this page for the ingredients highest in protein
What is potassium?
Potassium is an essential metallic element. In its natural state potassium has a soft silvery appearance and tarnishes quickly in air and it is rather beautiful1.
What is potassium?
Potassium is an essential metallic element. In its natural state potassium has a soft silvery appearance and tarnishes quickly in air and it is rather beautiful1.
In the body it acts as an electrolyte that can conduct electricity which is vital for several important biological functions2.
Why does it matter to me?
- Potassium is vital to ensure that your brain and spinal cord, known as our central nervous system (CNS), communicates messages to and from all the organs of your body. This process is called the generation and propagation of an ‘action potential’ and it depends exclusively on the presence of both potassium and sodium3.
- Since the CNS is what detects and responds to the bewildering array of stimuli in your environment potassium is vital to ensure that your CNS is in prime condition4.
- Potassium is key to stimulating the normal contraction and relaxation of muscles. However, it is also becoming increasingly clear that potassium is an important part of the physiological mechanism regulating skeletal muscle growth in response to intense exercise5.
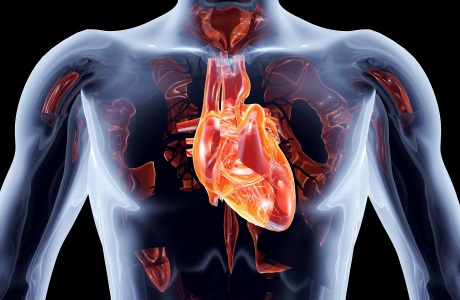
- The most important muscle in your body is your heart and potassium is vital to maintain its health. There is an extensive and compelling literature which strongly suggests that consuming the recommended amount of potassium through your diet can promote good cardiovascular health6.
What happens if I don’t get enough?
The RDA for potassium is extremely high and it can be difficult to obtain enough from the diet. Recent estimates strongly suggest that a large majority of those living in developed societies do not which may give rise to health consequences7.
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
Evidence strongly suggests that consumption of a diet that consistently fails to provide the RDA of potassium will increase your blood pressure (hypertension). Hypertension is a significant contributing factor to stroke and other forms of CVD. This is perhaps the most compelling reason to ensure that your diet is healthy, varied and balanced and provides a substantial amount of potassium8.
‘Obesity’ is the primary risk factor for type 2 diabetes. However, from a nutritional perspective, the term ‘obesity’ is just a catch all for a variety of metabolic changes that occur when you are overweight.
Potassium is integral to the way in which the CNS communicates to all the organs of the body, even when its subliminal. Therefore, it is partly responsible for ensuring that insulin is secreted from pancreatic cells when the need arises (when there is too much sugar in the blood).
Consequently, a reduction in the amount of available potassium may reduce insulin secretion which may give rise to elevated levels of glucose in the blood stream. This is sometimes described as ‘glucose intolerance’ or ‘hyperglycaemia’.
Observational studies suggest that potassium status is linked to blood glucose control and type 2 diabetes. However, this association has not been adequately evaluated in randomised control trials (RCTs) which may be too difficult to conduct because of ethical issues9,10.
How much do I need?
Potassium has the highest RDA (recommended dietary amount) of any vitamin or mineral.
The RDA (average daily intake to protect health for 98% of the population) for potassium is an AI (adequate intake) this is due to a lack of comprehensive data to arrive at an RDA. An AI is assumed to be at the level of an RDA or above it.
The RDA of 4.7 grams a day is associated with a reduction in the risk of several chronic diseases.
Review date: 11/15/2023
Next review date: 11/15/2024
291
445
https://www.checkyourfood.com/content/blob/Micronutrients/top-foods-for-Potassium.jpg
Top 6 ingredients for Potassium taking into account portion size and cooking retention factors
Filter ingredients by:

 About nutrients
About nutrients
 All nutrients
All nutrients
 vitamins
vitamins
 minerals
minerals
 phytochemicals
phytochemicals
 fatty acids
fatty acids
 macronutrients
macronutrients
 amino acids
amino acids